Domain restriction
Adapted from OpenStax Calculus Volume 11
We have seen that with domain does not have an inverse function because it is not one-to-one.
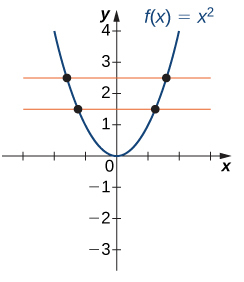
However, we can choose a subset of the domain of such that the function is one-to-one. We call this subset a restricted domain.
For example, we can define new functions and such that they both share the same rule as but have smaller domains. Each of them is one-to-one and has an inverse.
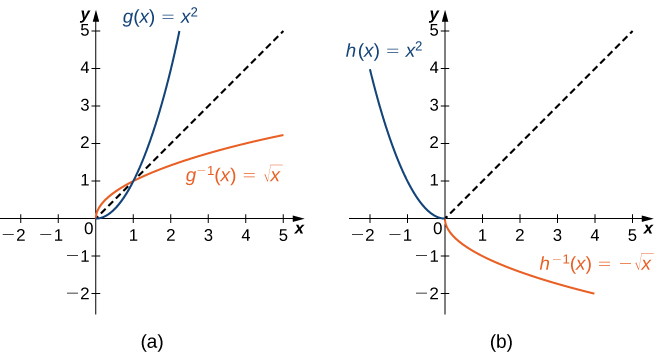
-
Content in this page is adapted from OpenStax Calculus Volume 1 by Gilbert Strang and Edwin “Jed” Herman under the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Sharealike 4.0 License.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/calculus-volume-1/pages/1-4-inverse-functions↩︎