Hyperbolas
Adapted from OpenStax College Algebra 2e1
Equations of hyperbolas
Horizontal and vertical hyperbolas have the following equations in standard form
Key features of hyperbolas
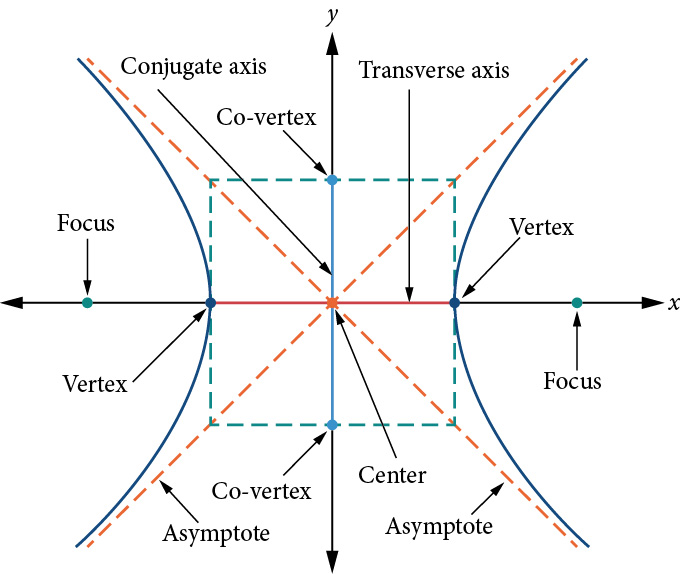
The diagram above shows the key features of hyperbolas. In particular, the following features are most useful in drawing hyperbolas:
- center
- vertices
- asymptotes
Drawing a hyperbola
Center
Just like in drawing an ellipse, we draw a hyperbola by first identifying its center. For an equation of standard form above, the center has coordinates
Horizontal vs vertical hyperbolas
We then deduce whether our hyperbola is horizontal or vertical, based on its equation (does or appear first in the difference in our equation?).
Vertices
We then locate the vertices. For a horizontal hyperbola, the two vertices are units on the left and right of the center, with coordinates and
For a vertical hyperbola, the two vertices are units above and below the center, with coordinates and
Asymptotes
For both horizontal and vertical hyperbolas, there are two oblique asymptotes that pass through the center. They have gradient so their equations are
With these features set up on our graph, we can then proceed to draw our hyperbolas. We start off at one corner of an asymptote, bend towards and pass through the vertex and then go back towards the other asymptote.
We draw to the left and right of the center for,horizontal hyperbolas. For vertical hyperbolas, we draw above and below the center.
Example 1
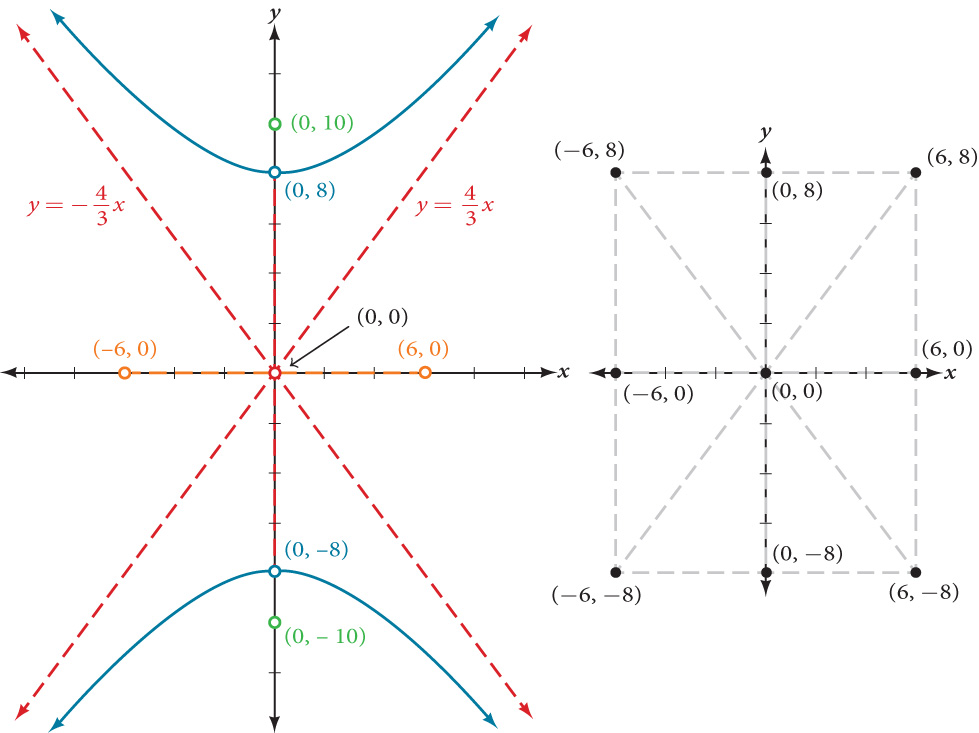
The following is a sketch of the vertical hyperbola with equation
The origin is the center of the hyperbola, with vertices and
The gradient of the asymptotes are so the equations of the asymptotes are
Example 2
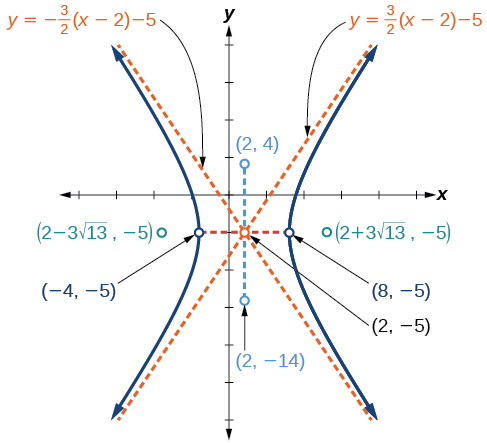
The following is a sketch of the horizontal hyperbola with equation
The center of the hyperbola is and it has vertices units horizontally from the center so their coordinates are and
The gradient of the asymptotes are so the equations of the asymptotes are
-
Content in this page is adapted from OpenStax College Algebra 2e by Jay Abramson under the Creative Commons Attribution License.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra-2e/pages/5-6-rational-functions↩︎